An ingrown hair under the skin, medically termed pseudofolliculitis barbae, occurs when a shaved or plucked hair curls back and grows into the skin.
This condition commonly affects areas with coarse, curly hair, such as the beard, scalp, or bikini line. It can cause inflammation, pain, and scarring.
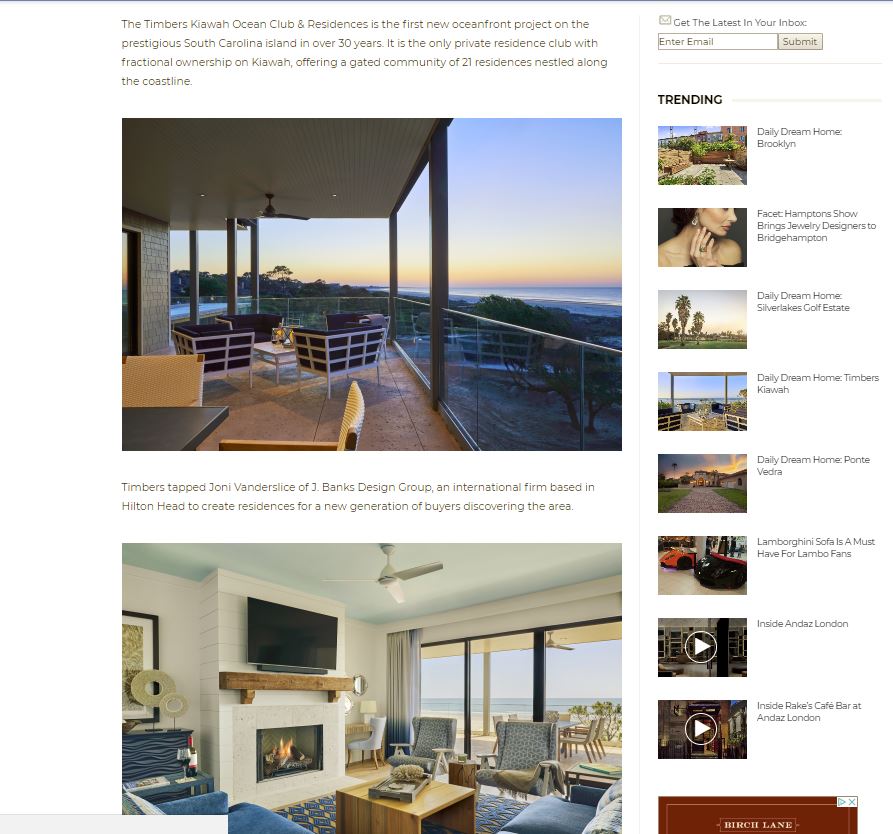
Ingrown hairs have significant relevance in dermatology, affecting individuals globally. Understanding their causes and effective treatments is crucial for maintaining skin health. Historically, advancements in laser hair removal have provided promising solutions for reducing the prevalence of ingrown hairs.
Ingrown Hair Under Skin
Understanding the essential aspects of ingrown hair under skin is vital for managing this common skin condition. These key aspects encompass:
- Causes: Shaving or plucking coarse, curly hair
- Symptoms: Inflammation, pain, scarring
- Treatment: Laser hair removal, topical creams
- Prevention: Proper shaving techniques
Each of these aspects plays a crucial role in developing a comprehensive understanding of ingrown hairs. Understanding the causes helps identify risk factors, while recognizing symptoms enables early detection and treatment. Treatment options, including laser hair removal, provide effective solutions for reducing the prevalence of ingrown hairs. Additionally, preventive measures, such as proper shaving techniques, are essential for minimizing the occurrence of this condition.
Causes
Shaving or plucking coarse, curly hair is a primary cause of ingrown hairs. The sharp edges of shaved or plucked hair can easily curl back into the skin, leading to inflammation and pain. Coarse and curly hair is more prone to ingrown hairs because it is more likely to curl back into the skin after being shaved or plucked.
The relationship between shaving or plucking coarse, curly hair and ingrown hairs is well-established. Studies have shown that individuals with coarse, curly hair are more likely to experience ingrown hairs after shaving or plucking. This is especially true for individuals who shave or pluck their hair frequently.
Understanding the connection between shaving or plucking coarse, curly hair and ingrown hairs has important practical applications. By identifying the cause of ingrown hairs, individuals can take steps to prevent or reduce their occurrence. For example, individuals with coarse, curly hair may want to avoid shaving or plucking their hair too frequently. They may also want to use shaving cream or gel to help reduce the risk of ingrown hairs.
Symptoms
Ingrown hairs can lead to a range of symptoms, including inflammation, pain, and scarring. These symptoms can vary in severity, and they can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life.
-
Inflammation
Inflammation is a common symptom of ingrown hairs. It occurs when the body's immune system responds to the presence of the foreign hair under the skin. Inflammation can cause the skin to become red, swollen, and painful. -
Pain
Pain is another common symptom of ingrown hairs. The pain can range from mild to severe, and it can be made worse by pressure or friction. In some cases, the pain can be so severe that it makes it difficult to walk or sit. -
Scarring
Scarring is a less common but more serious symptom of ingrown hairs. Scarring occurs when the inflammation caused by the ingrown hair damages the skin. Scars can be permanent, and they can cause significant cosmetic concerns.
The symptoms of ingrown hairs can be a significant nuisance, and they can have a negative impact on an individual's quality of life. In some cases, ingrown hairs can even lead to infection. If you are experiencing symptoms of ingrown hairs, it is important to see a doctor to rule out any other underlying medical conditions.
Treatment
The treatment options for ingrown hairs encompass laser hair removal and topical creams, each offering distinct approaches to address the underlying causes and symptoms.
-
Laser Hair Removal
Laser hair removal involves directing concentrated beams of light onto the hair follicles, destroying them and preventing future hair growth. This method is particularly effective for individuals with coarse, curly hair, as it targets the hair at its root, reducing the likelihood of ingrown hairs. -
Topical Creams
Topical creams containing ingredients such as salicylic acid or glycolic acid can help exfoliate the skin, unclog hair follicles, and reduce inflammation. These creams can be applied directly to the affected areas to soothe irritation and prevent the formation of ingrown hairs.
The choice of treatment for ingrown hairs depends on the severity of the condition and the individual's preferences. Laser hair removal provides a long-term solution by permanently reducing hair growth, while topical creams offer a more immediate relief from symptoms. Consulting with a dermatologist can help determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the specific needs of each patient.
Prevention
Prevention plays a crucial role in minimizing the occurrence of ingrown hairs, with proper shaving techniques being a key aspect. By adhering to these techniques, individuals can effectively reduce the risk of developing this common skin condition.
-
Use a sharp razor
A sharp razor ensures a clean, close shave without tugging or pulling at the hair. This reduces the likelihood of the hair breaking off below the skin's surface, which can lead to ingrown hairs.
-
Shave in the direction of hair growth
Shaving against the grain can irritate the skin and increase the chances of ingrown hairs. Shaving in the direction of hair growth allows the razor to glide smoothly over the skin, minimizing irritation.
-
Exfoliate before shaving
Exfoliating the skin prior to shaving removes dead skin cells and allows the razor to reach the hair follicles more effectively. This helps prevent ingrown hairs by ensuring that the hair can grow out of the skin without obstruction.
-
Moisturize after shaving
Moisturizing after shaving helps soothe the skin and reduce irritation. It also helps prevent the skin from becoming dry and flaky, which can increase the risk of ingrown hairs.
By following these proper shaving techniques, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing ingrown hairs. These techniques help ensure a clean, close shave without causing irritation or damage to the skin. Incorporating these practices into a regular shaving routine can help maintain healthy, smooth skin.
FAQs on Ingrown Hair Under Skin
This FAQ section aims to address common questions and clarify various aspects related to ingrown hair under the skin.
Question 1: What causes ingrown hair?
Ingrown hair occurs when shaved or plucked hair curls back and grows into the skin. It commonly affects areas with coarse, curly hair, such as the beard, scalp, or bikini line.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of ingrown hair?
Ingrown hair can cause inflammation, pain, and scarring. The affected area may appear red, swollen, and painful.
Question 3: How can I prevent ingrown hair?
Proper shaving techniques can help prevent ingrown hairs. Use a sharp razor, shave in the direction of hair growth, exfoliate before shaving, and moisturize after shaving.
Question 4: What are the treatment options for ingrown hair?
Treatment options include laser hair removal and topical creams. Laser hair removal permanently reduces hair growth, while topical creams help exfoliate the skin and reduce inflammation.
Question 5: Can ingrown hair lead to infection?
In severe cases, ingrown hair can become infected. If you experience severe pain, swelling, or discharge, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Question 6: How can I manage ingrown hair at home?
Home remedies for ingrown hair include applying warm compresses, exfoliating the skin, and using over-the-counter antiseptic solutions. However, if home remedies do not provide relief, seeking professional treatment is advisable.
These FAQs provide essential information on ingrown hair under the skin, covering causes, symptoms, prevention, treatment, and home management. Understanding these aspects can help individuals effectively address and manage this common skin condition.
Moving forward, we will delve deeper into the medical management of ingrown hair, exploring advanced treatment options and discussing when professional intervention is necessary.
Tips for Managing Ingrown Hairs
This section provides practical tips to help manage ingrown hairs effectively.
Tip 1: Use Proper Shaving Techniques
Employ sharp razors, shave in the direction of hair growth, exfoliate beforehand, and moisturize afterward to minimize irritation and prevent ingrown hairs.
Tip 2: Exfoliate Regularly
Exfoliation removes dead skin cells, allowing ingrown hairs to break through the skin's surface. Use gentle scrubs or chemical exfoliants to avoid irritation.
Tip 3: Apply Warm Compresses
Warm compresses help soften the skin and reduce inflammation. Apply a warm washcloth to the affected area for 10-15 minutes several times a day.
Tip 4: Use Antibacterial Soap
Keep the affected area clean to prevent infection. Wash with antibacterial soap and pat dry gently.
Tip 5: Avoid Tight Clothing
Tight clothing can rub against the skin and irritate ingrown hairs. Wear loose, comfortable clothing to minimize friction.
Tip 6: Use Over-the-Counter Treatments
Salicylic acid or glycolic acid creams can help exfoliate the skin and reduce inflammation. Follow the instructions carefully to avoid irritation.
Tip 7: Seek Professional Help if Needed
If home remedies do not provide relief or the ingrown hair becomes infected, consult a dermatologist for professional treatment.
By following these tips, you can effectively manage ingrown hairs and maintain healthy, smooth skin.
In the next section, we will discuss advanced treatment options for ingrown hairs, exploring laser hair removal and other medical interventions.
Conclusion
Our exploration of ingrown hair under skin has shed light on its causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment. Understanding the underlying factors that contribute to ingrown hairs, such as shaving or plucking coarse, curly hair, is crucial for effective management.
Key takeaways include:
- Proper shaving techniques, regular exfoliation, and good skin hygiene can help prevent ingrown hairs.
- Home remedies like warm compresses and antibacterial soap can alleviate symptoms, while OTC treatments provide further relief.
- Advanced treatments such as laser hair removal offer long-term solutions for persistent ingrown hairs.
Managing ingrown hair under skin requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both prevention and treatment. By implementing these strategies, individuals can maintain healthy skin and minimize the discomfort associated with this common condition.

No comments:
Post a Comment